Physical Sciences is often considered one of the hardest subjects in Matric. It is a two-paper subject that demands two completely different skill sets: the mathematical logic for Physics (Paper 1) and the memorization and conceptual understanding for Chemistry (Paper 2).
In my experience, students who get distinctions aren’t just “smart”; they know exactly how the examiners mark the papers. This guide breaks down the curriculum based on the Examination Guidelines and highlights the specific traps you need to avoid.
Paper 1: Physics (150 Marks)
Physics is about applying laws to real-world situations. You cannot just memorize definitions; you must know how to apply them when the context changes.
- Mechanics (±63 Marks)
This is the biggest section of the paper. If you master Mechanics, you pass the paper.
- Newton’s Laws:
- Newton 1 & 2: The most common mistake here is forgetting that Force is a vector. When using F_{net} = ma , you must choose a positive direction (e.g., “Right is Positive”). If a force acts to the left, it must be negative.
- Free Body Diagrams: This is the foundation of Mechanics. If your diagram is wrong, your calculation will be wrong. (See my tips below on how to draw these perfectly).
- Work, Energy & Power:
- The Work-Energy Theorem: W_{net} = \Delta K . This theorem connects force and velocity. It is your “get out of jail free” card when you don’t have time.
- Conservation of Energy: Be careful! You can only use this when there is no friction or air resistance. If there is friction, energy is lost to heat, and you must use the Work-Energy Theorem instead.
- Momentum & Impulse:
- Conservation of Momentum: This applies to collisions (cars crashing) and explosions (guns firing). Remember: Total momentum before = Total momentum after.
- Waves, Sound & Light (±17 Marks)
- The Doppler Effect: This describes the change in frequency when a source (like an ambulance) moves relative to a listener.
- The Tricky Part: The formula f_L = \frac{v \pm v_L}{v \pm v_S} f_S is given, but the signs (+ or -) are not.
- Rule of Thumb: If the source moves towards the listener, the frequency must increase. To make the answer bigger, you subtract from the bottom (denominator).
- Blue Shift vs. Red Shift: Know the application for light (stars moving away appear “Red”).
- Electricity & Magnetism (±55 Marks)
- Electric Circuits:
- Internal Resistance: This is why the voltage reading on a battery drops when you close the switch (“lost volts”). You need to treat the battery itself as a resistor.
- Series vs. Parallel: Remember the basics—Current splits in parallel; Voltage splits in series.
- Electrodynamics:
- Motors vs. Generators: You must be able to tell them apart just by looking at a diagram.
- Motor: Has a battery connected ( \text{Electrical energy} \rightarrow \text{Mechanical energy} ).
- Generator: Has no battery; it is being turned ( \text{Mechanical energy} \rightarrow \text{Electrical energy} ).
- AC vs. DC: Know the difference between Split Rings (DC) and Slip Rings (AC).
- Motors vs. Generators: You must be able to tell them apart just by looking at a diagram.
Paper 2: Chemistry (150 Marks)
Chemistry is about molecules and how they react. While Physics requires calculation, Chemistry requires precise language.
- Organic Chemistry (±54 Marks)
This is a huge section, but it is very “learnable.” If you study this well, these are guaranteed marks.
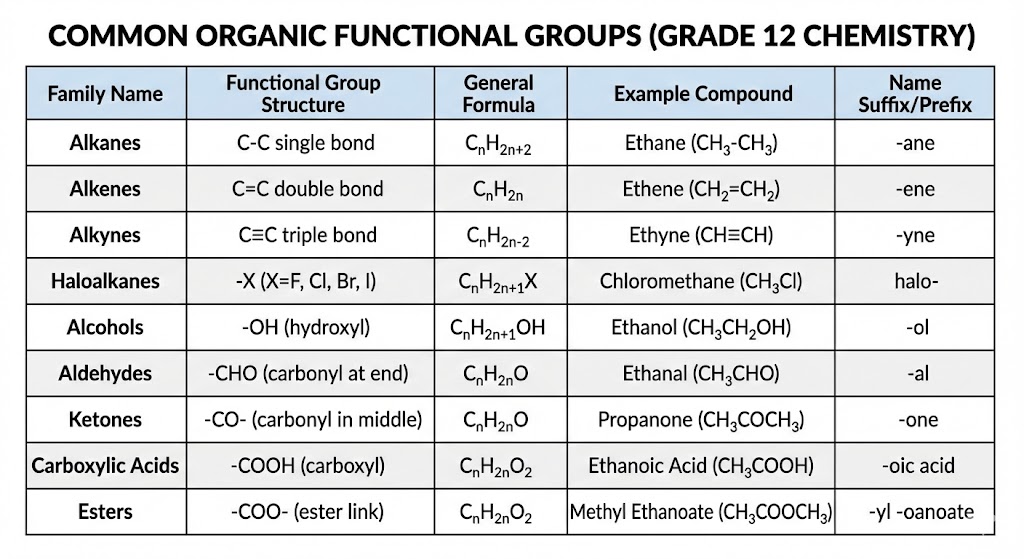
- Nomenclature (Naming): You must learn the IUPAC rules perfectly. Don’t mix up your suffixes (e.g., -ol for alcohols, -oic acid for carboxylic acids).
- Physical Properties: Examiners love asking why one compound boils at a higher temperature than another.
- The Answer Structure: Always identify the Intermolecular Force (IMF). Hydrogen bonds are stronger than Van der Waals forces. Stronger forces require more energy to overcome, leading to a higher boiling point.
- Reactions: You need to know the specific conditions (heat, catalyst, water) for Substitution, Addition, and Elimination reactions.
- Rate and Extent of Reaction (±23 Marks)
- Rates of Reaction: How do we speed up a reaction? You can increase Temperature, Concentration, Surface Area, or add a Catalyst. You must explain why using the Collision Theory (more effective collisions per unit time).
- Chemical Equilibrium:
- Le Chatelier’s Principle: This is 100% guaranteed to be in the exam. You will be asked to explain a shift in equilibrium. (See my “Bullet-Proof” structure in the tips section below).
- Chemical Change (±43 Marks)
- Acids & Bases: Practice your pH calculations and titration problems.
- Electrochemical Cells:
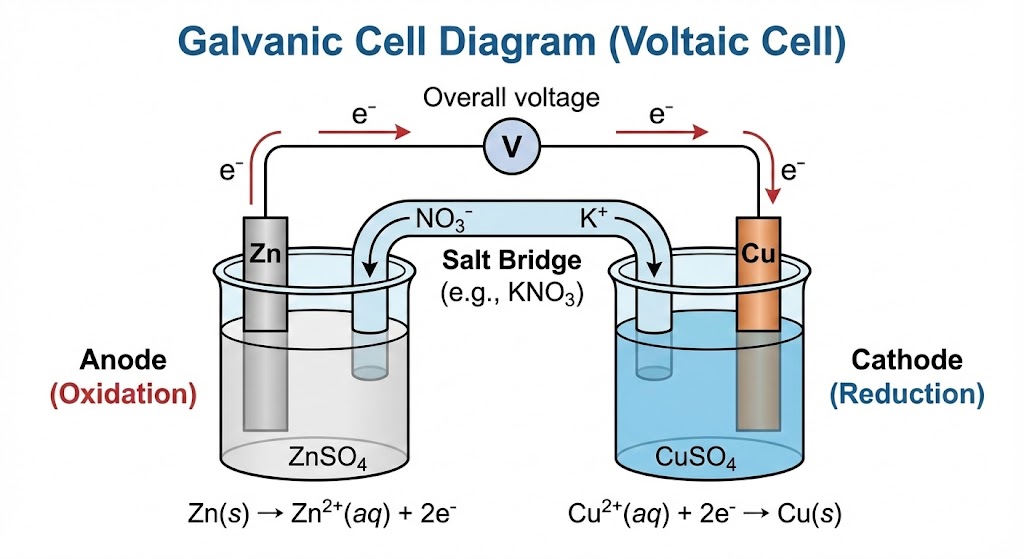
- Galvanic Cells: These act as batteries ( \text{Chemical} \rightarrow \text{Electrical} ). The Anode is where Oxidation happens (An Ox), and the Cathode is where Reduction happens (Red Cat).
- Electrolytic Cells: These use electricity to split chemicals (e.g., isolating Chlorine gas). Unlike Galvanic cells, these require a power source.
- Chemical Systems (±15 Marks)
- Fertilizers: Focus on the N-P-K ratios.
- Eutrophication: This is an environmental question. You need to explain how excess fertilizer washes into rivers, causes algae blooms, blocks sunlight, and kills fish by depleting oxygen.
Decksh’s Top 3 Tips for Distinction
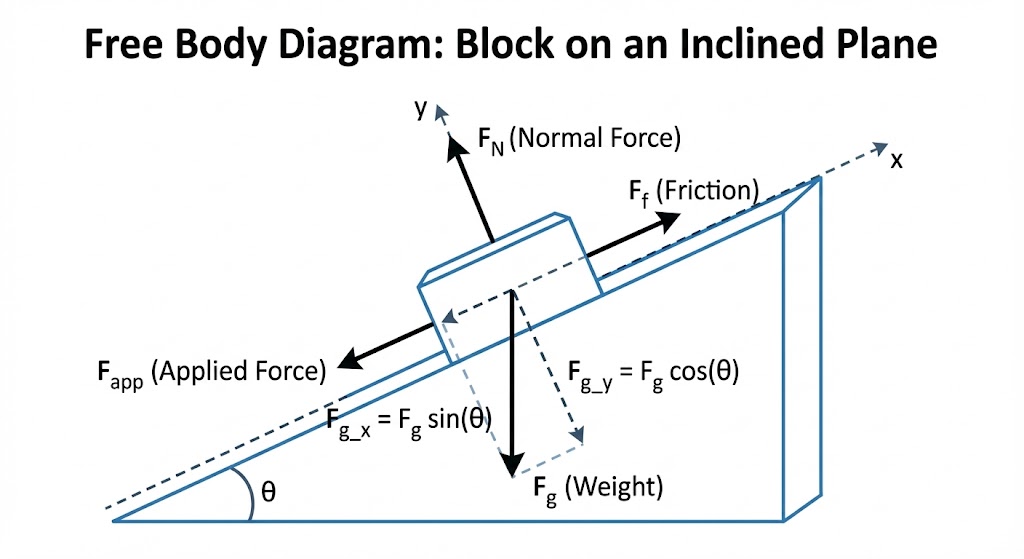
1. Master the “Free Body Diagram”
In Paper 1, you will be asked to draw forces acting on an object. This seems easy, but students lose silly marks here.
- Arrow Heads: Every line must have an arrow.
- Touching the Dot: The tail of the arrow must touch the dot (the object).
- Labels: Use standard labels like F_g (Gravity), N (Normal), and f_k (Friction). Do not invent your own abbreviations.
2. The “Bullet-Proof” Le Chatelier Answer
In Chemistry, when asked to explain an equilibrium shift, use this exact template to ensure you get full marks:
- Identify the Disturbance: “The temperature was increased…”
- State the System’s Response: “According to Le Chatelier, the system opposes the disturbance by trying to cool down…”
- Identify the Favoured Reaction: “Therefore, the endothermic reverse reaction is favoured.”
- State the Result: “Consequently, the yield of products decreases.”
3. Definitions are “Free Marks”
Both Physics and Chemistry have very specific definitions (e.g., “Work done by a net force” or “Homologous series”).
- The Rule: Memorize them word-for-word from the Exam Guidelines.
- Warning: Do not paraphrase. If you miss the keyword “net” in a force definition, you lose the mark.
Conclusion
Physical Sciences is tough, but it is logical.
For Paper 1, practice your calculations until you are comfortable with your calculator.
For Paper 2, focus on your definitions and naming organic molecules.
Good luck with your Matric Finals!

Very helpful thank you.